Google Search Console is a powerful, free tool that can help online store owners have a healthy, search-engine-friendly website.
It was created to help you monitor and maintain your site’s presence in Google search results by alerting you to errors, security issues, and indexing problems that may affect your search rankings. Search Console is the only place to get search engine optimization (SEO) information about your website directly from Google.
That being said, it can take some time to learn how to use it effectively. So, to help you get started, we’ve put together a guide of the key elements that can help improve your online store’s visibility.
Initial Steps:
In order to take advantage of Google Search Console, you must first sign up for a free account. Navigate to the Google Search Console website and click the blue “Start Now” button.
You’ll need to be signed into your existing Google/Gmail account or create a new one. Then, select which property type you’d like to use and enter your website’s URL. Here are the available property types:

Domain:
- Covers all versions of your URL (http://, https://, http://www, https://www, subdomains, etc.)
- Requires modifying the DNS settings of your domain name for verification.
URL Prefix:
- Covers only a specific prefix. For example, it would cover only https://example.com but NOT http://example.com. You may want to create separate accounts for each prefix if you choose to take this route.
- Offers a variety of simpler verification methods.
After you choose an option, you’ll need to move forward with verifying website ownership. Google provides specific instructions for verifying your domain here.
To confirm that your URL is verified, click Settings in the left-hand menu. Beside Ownership Verification, there should be a green check mark and the text, “You are a verified owner.”

Adding Users:
If you’re collaborating with a team or hiring someone to help you with SEO or marketing, you’ll need to add each person as a user on your account.
To do this, choose the Users & Permissions tab and click the blue Add User button in the top right hand corner.
Note: The user has to have a valid Google account.

After you input their email address, you can also choose their permissions level – Full or Restricted. You can always change their access level and/or delete them altogether.
Adding an XML Sitemap:
An XML sitemap tells search engines what pages are on your website, how they’re related to one another, when they were last updated, and how important each one is relative to other URLs.
Adding an XML sitemap doesn’t give you a boost in search rankings, but it does help search engine bots crawl your website and index your content more efficiently.
XML sitemaps are not created on WordPress automatically, but all you need to do is activate the free Jetpack plugin and enable Sitemaps. This will generate an XML sitemap for your website without any additional steps, but you can customize it with additional post types if you’d prefer.
To verify this, go to example.com/sitemap.xml. (Don’t forget to replace example.com with your own URL.) If everything is set up correctly, you should see a page with the title XML sitemap and a list of information.
The next step is to tell Google Search Console where it can find your sitemap.
In the Google Search Console left-hand menu, click on Sitemaps and paste the last part of the URL sitemap.xml in the box. Then, click the blue Submit button.
You should see your website’s sitemap populate in the lower section under Submitted Sitemaps.

Google Search Console will check your sitemap and use it to improve their indexing process.
Understanding Errors:
One of the benefits of Google Search Console is that you’ll receive notifications about indexing errors that could affect your search engine rankings.
To see if you have any errors, click Coverage in the left-hand menu. This report will show you which pages on your website are indexed by Google and which pages result in an error or warning. Scroll to see a list of specific errors and click each one to find out more details.
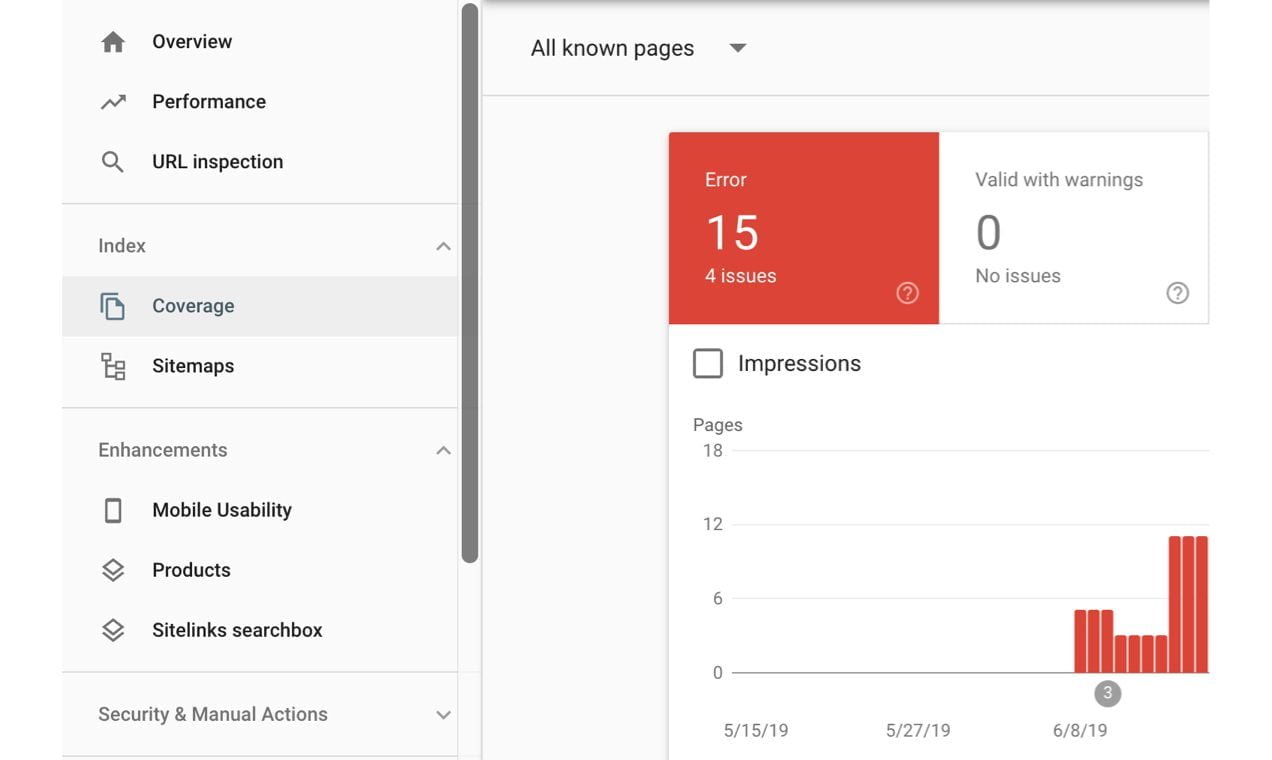
After you attempt to fix an error, navigate back to the error details and click Validate Fix. Google will then recrawl the page and indicate whether or not the issue was resolved.

Remember that not all errors are created equally, which is why it’s so important to view the details. Some can be safely ignored while others will require your immediate attention.
Some of the most common errors are:
Server Error (5xx). This means that something with your server prevented Google from loading the page (URL). This could be due to heavy traffic, server maintenance, or a number of other causes. Double-check this URL and see if the error still occurs. If it doesn’t, it could have been taken care of on its own. If it does, you may need to contact your hosting company.
Redirect Error. This means that a redirect you created doesn’t work. This often results from entering your domain/URL incorrectly.
Submitted URL Blocked by Robots.txt. This means that Google bots can’t crawl the page because of a setting in your Robots.txt file. There are reasons to intentionally block certain pages, but if this error is accidental, you may need to remove the block manually so that it shows up in search results.
Submitted URL Marked ‘Noindex’. This means that you’ve submitted this page to Google for indexing, but the page has been labeled ‘noindex’ either in a meta tag or HTTP response. If you’re using the Yoast SEO plugin, double-check the page’s SEO settings to verify/fix this.
Submitted URL Not Found (404). This means that the page you’ve submitted doesn’t exist on your website. Find more information on how to fix this in the section below!
Fixing 404 Errors:
A 404 error is one of the most common errors in Google Search Console and appears when you link to a nonexistent page.
This could happen if you change your permalink structure in WordPress, change the page slug after the post has been published, or delete a page, post, or product.
To fix the error, redirect the nonexistent URL to a new or similar page. You can either create a 301 redirect in your .htaccess file or use the free WordPress plugin, Redirection.
Once you do that, click on the error in Google Search Console and choose Validate Fix.
Submit a Crawl Request:
Submitting a crawl request is an extremely useful part of Google Search Console. It allows you to send a request to Google to fetch and index/reindex a new or updated page (URL).
Why is this important?
Let’s say you’ve updated one of your popular blog posts to make it even better, but the Google snippet showing up in search results is highlighting old information. You can submit a crawl request to have Google recrawl that page and index the updated information.
This also comes in handy when changing SEO titles and descriptions and adding new content, landing pages or products to your online store.
How do you submit a crawl request?
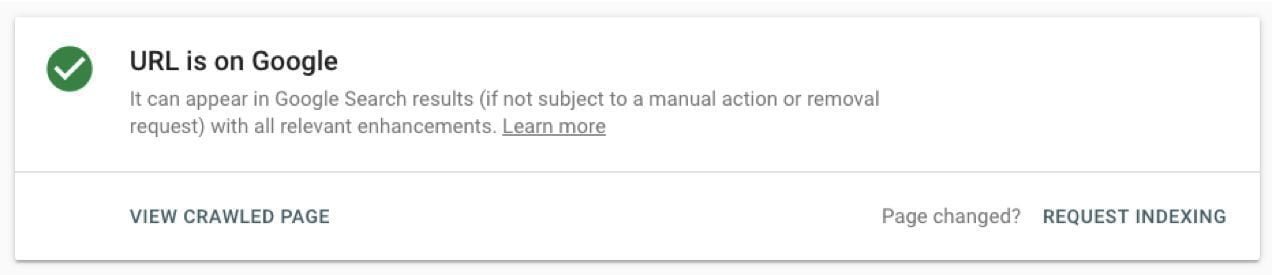
Paste the URL that you’d like crawled or recrawled in the box at the top of any page.
Once Google Search Console inspects the URL, you can click Request Indexing to let Google search bots know that the content on the page has been updated and needs to be recrawled.
Start Improving with Google Search Console:
No matter what you sell or the size of your online store, you should have a Google Search Console account set up. It’s completely free, and was created by Google to help you, your website traffic, and, ultimately, your customers.
But remember, Google Search Console doesn’t do anything on its own for your website. Setting it up does not mean that you’re going to instantly get more traffic or improve your SEO.
Like any tool, you’ll need to spend some time learning how to use it to take full advantage of the information it provides. However, it’s absolutely worth the effort to improve the search engine visibility of your online store!

